Check out the scientific names for fish species
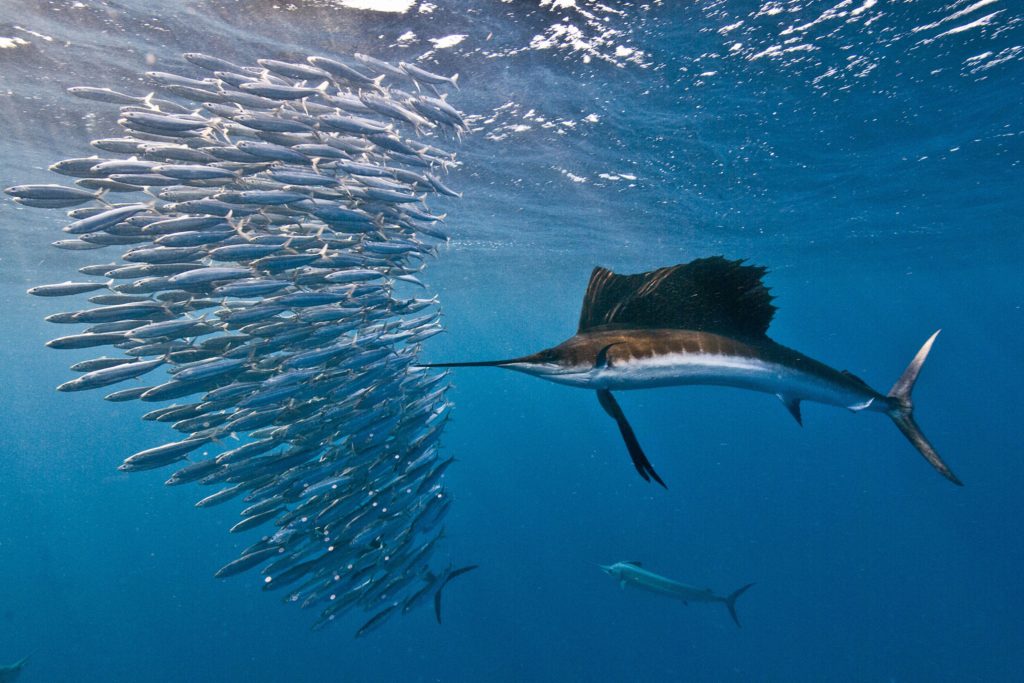
Fish, any of around 34,000 types of vertebrate creatures (phylum Chordata) found in the new and salt waters of the world. Living species range from the crude jawless lampreys and hagfishes through the cartilaginous sharks, skates, and beams to the bountiful and various hard fishes. Most fish species are relentless; in any case, one animal group, the opah (Lampris guttatus), is warm-blooded.
The term fish is applied to an assortment of vertebrates of a few transformative lines. It depicts a day-to-day existence structure as opposed to scientific classification. As individuals from the phylum Chordata, fish share certain provisions with different vertebrates.
These provisions are gill cuts sooner or later in the existence cycle, a notochord, or skeletal supporting pole, a dorsal empty nerve line, and a tail. Living fishes address around five classes, which are as particular from each other just like the four classes of natural air-breathing creatures—creatures of land and water, reptiles, birds, and warm-blooded animals.
For instance, jawless fishes (Agnatha) have gills in pockets and need appendage supports. Surviving agnathans are the lampreys and the hagfishes. As the name infers, the skeletons of fishes of the class Chondrichthyes (from chondr, “ligament,” and ichthys, “fish”) are made completely of the ligament.
Current fish of this class come up short on a dip bladder, and their scales and teeth are comprised of similar placoid material. Sharks, skates, and beams are instances of cartilaginous fishes.
The hard fishes are by a long shot the biggest class. Models range from the minuscule ocean pony to the 450-kg (1,000-pound) blue marlin, from the leveled soles and struggle to the square-shaped puffers and sea sunfishes.
In contrast to the sizes of the cartilaginous fishes, those of hard fishes, when present, develop all through life and are comprised of slender covering plates of bone. Hard fishes likewise have an operculum that covers the gill cuts.

The investigation of fishes, the study of ichthyology, is of expansive significance. Fishes are important to people for some reasons, the most significant being their relationship with and reliance on the climate.
A more clear justification behind premium in fishes is their job as a moderate however significant piece of the world’s food supply. This asset, when thought limitless, is currently acknowledged to be limited and insensitive offset with the natural, substance, and actual components of the amphibian climate.
Overfishing, contamination, and change of the climate are the main foes of appropriate fisheries on the board, both in new waters and in the sea. (For a definite conversation of the innovation and financial matters of fisheries, see business fishing.) Another down-to-earth justification behind concentrating on fishes is their utilization in infection prevention. As hunters on mosquito hatchlings, they assist with checking jungle fever and other mosquito-borne infections.
The warm-bloodedness of the opah (Lampris guttatus) results from a warmth trade framework in the fish’s gills. The warmth produced by muscle development is moved in deoxygenated blood to the gills, which disperse the warmth to oxygenated blood, which is then siphoned by the heart to the remainder of the fish’s body.
Fishes are significant lab creatures in numerous parts of clinical and organic exploration. For instance, the status of many fishes to adapt to imprisonment has permitted scientists to concentrate on conduct, physiology, and even biology under generally normal conditions.

Fishes have been particularly significant in the investigation of creature conduct, where research on fishes has given an expansive base to the comprehension of the more adaptable conduct of the greater vertebrates. The zebrafish is utilized as a model in investigations of quality articulation.
There are tasteful and sporting explanations behind an interest in fish. A large number of individuals keep live fishes in home aquariums for the straightforward joy of noticing the excellence and conduct of creatures in any case new to them.
Aquarium fishes give an individual test to numerous aquarists, permitting them to test their capacity to keep a little part of the indigenous habitat in their homes. Sportfishing is one more method of partaking in the regular habitat, likewise enjoyed by a great many individuals consistently. Premium in aquarium fishes and sportfishing upholds multimillion-dollar businesses all through the world.
Harlequin fish (Rasbora heteromorpha).
Pencil fish (anostomus).
Primary variety
Fishes have been in presence for in excess of 450 million years, during which time they have developed over and again to squeeze into pretty much every possible sort of oceanic environment.
One might say, land vertebrates are just exceptionally changed fishes: when fishes colonized the land’s natural surroundings, they became tetrapod (four-legged) land vertebrates.
The well-known origination of a fish as a tricky, smoothed out sea-going creature that has blades and inhales by gills applies to many fishes, yet definitely, a bigger number of fishes go amiss from that origination than adjust to it.
For instance, the body is lengthened in many structures and significantly abbreviated in others; the body is smoothed in a few (basically in base dwelling fishes) and horizontally compacted in numerous others; the blades might be extravagantly broadened, framing complex shapes, or they might be decreased or even lost; and the places of the mouth, eyes, nostrils and gill openings change generally. Air breathers have shown up in a few transformative lines.

Clam toadfish (Opsanus tau)
Many fishes are secretively shaded and molded, intently coordinating with their separate surroundings; others are among the most splendidly hued of all organic entities, with a wide scope of tints, frequently of striking power, on a solitary person.
The splendor of colors might be upgraded by the surface construction of the fish, with the goal that it nearly appears to sparkle. Various disconnected fishes have genuine light-creating organs. Many fishes can adjust their shading—some with the end goal of disguise, others for the upgrade of social signs.
Fishes range in grown-up length from under 10 mm (0.4 inches) to in excess of 20 meters (60 feet) and in weight from about 1.5 grams (under 0.06 ounces) to a large number of kilograms.
Some live in shallow warm springs at temperatures somewhat over 42 °C (100 °F), others in chilly Arctic oceans a couple of degrees under 0 °C (32 °F) or in cool profound waters in excess of 4,000 meters (13,100 feet) underneath the sea surface.
The underlying and, particularly, the physiological transformations for life at such limits are moderately inadequately known and furnish the deductively inquisitive with extraordinary motivation for study.