Holliday junction: All you need to think about cross-molded design that structures during the course of hereditary recombination
A Holliday junction is a fanned nucleic corrosive design that contains four twofold abandoned arms consolidated. These arms might embrace one of a few compliances relying upon support salt focuses and the succession of nucleobases nearest to the junction. The design is named after Robin Holliday, the atomic scholar who proposed its reality in 1964.
Holliday junction, cross-molded construction that structures during the course of hereditary recombination, when two twofold abandoned DNA particles become isolated into four strands to trade fragments of hereditary data. This construction is named after British geneticist Robin Holliday, who proposed the first model for homologous (or general) recombination in 1964.
Homologous recombination happens during meiosis and is portrayed by the trading of qualities between a maternal chromatid and a fatherly chromatid of a homologous chromosome pair.
The two-parent DNA atoms, which have a significant length of comparative base arrangements, are isolated into single strands, bringing about base blending that prompts a four-abandoned DNA structure. The Holliday junction goes along the DNA duplex by “unfastening” one strand and improving the hydrogen bonds on the subsequent strand.
In science, Holliday junctions are a critical middle of the road in many kinds of hereditary recombination, just as in twofold strand break-fix. These junctions for the most part have an even grouping and are subsequently portable, implying that the four individual arms might slide through the junction in a particular example that to a great extent saves base matching. Furthermore, four-arm junctions like Holliday junctions show up in some practical RNA atoms.
Stationary Holliday junctions, with uneven successions that lock the strands in a particular position, were misleadingly made by researchers to concentrate on their construction as a model for normal Holliday junctions.
These junctions likewise later discovered use as fundamental underlying structure blocks in DNA nanotechnology, where various Holliday junctions can be joined into explicitly planned calculations that furnish atoms with a serious level of primary unbending nature.

Design
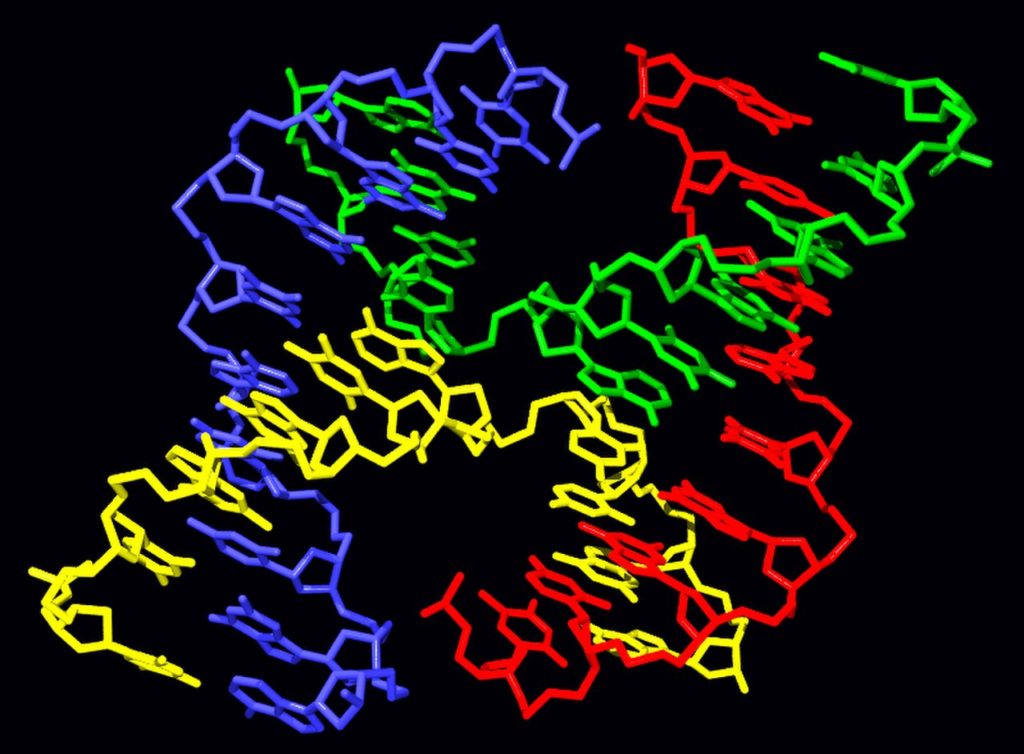
Atomic construction of a stacked Holliday junction, in which the four arms stack into two twofold helical areas. Note how the blue and red strands remain generally helical, while the green and yellow strands get over between the two areas.
Sub-atomic construction of an unstacked (open-X) Holliday junction. This adaptation needs base stacking between the twofold helical areas and is steady just in arrangements lacking divalent metal particles like Mg2+. From PDB: 3CRX.
Schematic graphs of the three base-stacking conformational isomers of the Holliday junction. The two stacked conformers vary in which sets of two arms are limited by coaxial stacking: at left, the stacks are red–blue and cyan–fuchsia, while at right the stacks are red-cyan and blue–maroon. The bases closest to the junction point figure out which stacked isomer overwhelms.
The unstacked structure is an almost square planar, expanded adaptation. Then again, the stacked conformers have two consistent twofold helical areas isolated by a point of about 60° in a right-gave heading. Two of the four strands stay generally helical, staying inside every one of the two twofold helical areas, while the other two cross between the two spaces in an antiparallel fashion.
The two potential stacked structures vary in which sets of the arms are stacked with one another; which of the two overwhelms is exceptionally reliant upon the base groupings closest to the junction.
A few successions bring about a balance between the two conformers, while others firmly favor a solitary conformer. Specifically, junctions containing the succession A-CC connecting the junction point appear to firmly incline toward the conformer that permits hydrogen to attach to shape between the subsequent cytosine and one of the phosphates at the junction point.
While most examinations have zeroed in on the characters of the four puts together closest to the junction with respect to each arm, it is obvious that bases further away can likewise influence the noticed stacking conformations.

Natural capacity
The Holliday junction is a critical middle in homologous recombination, an organic cycle that increments hereditary variety by moving qualities between two chromosomes, just as site-explicit recombination occasions including integrases.
They are moreover associated with the fix of twofold strand breaks. furthermore, cruciform designs including Holliday junctions can emerge to diminish helical strain in balanced arrangements in DNA supercoils.
While four-arm junctions additionally show up in practical RNA particles, for example, U1 spliceosomal RNA and the hair clip ribozyme of the tobacco ringspot infection, these normally contain unpaired nucleotides in the middle of the matched twofold helical areas and accordingly don’t stringently take on the Holliday structure.
The Holliday junctions in homologous recombination are between indistinguishable or almost indistinguishable groupings, prompting an asymmetric course of action of successions around the focal junction.
This permits a branch relocation cycle to happen where the strands travel through the junction point.[1] Cleavage, or goal, of the Holliday junction, can happen too.
Cleavage of the first arrangement of strands prompts two atoms that might show quality transformation yet not a chromosomal hybrid, while cleavage of the other arrangement of two strands makes the subsequent recombinant particles show hybrid. All items, paying little heed to cleavage, are heteroduplexes in the area of Holliday junction relocation.

Goal
In maturing yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Holliday junctions can be settled by four unique pathways that record for basically all Holliday junction goals in vivo.
The pathway that delivers most of the hybrids in S. cerevisiae sprouting yeast, and perhaps in well-evolved creatures, includes proteins EXO1, MLH1-MLH3 heterodimer (called MutL gamma), and SGS1 (ortholog of Bloom condition helicase).
The MLH1-MLH3 heterodimer ties especially to Holliday junctions.[13] It is an endonuclease that makes single-strand breaks in supercoiled twofold abandoned DNA.
The MLH1-MLH3 heterodimer advances the arrangement of hybrid recombinants.[15] While the other three pathways, including proteins MUS81-MMS4, SLX1, and YEN1, separately, can advance the Holliday junction goal in vivo, nonattendance of each of the three nucleases unobtrusively affects the development of hybrid items.
Use in DNA nanotechnology
This twofold hybrid (DX) supramolecular complex contains two Holliday junctions between the two twofold helical areas, on the top and the base in this picture. This tile is equipped for framing two-dimensional arrays.
Primary article: DNA nanotechnology
DNA nanotechnology is the plan and production of counterfeit nucleic corrosive constructions as designing materials for nanotechnology as opposed to as the transporters of hereditary data in living cells.
The field utilizes extended DNA structures as basic parts to make more intricate, judiciously planned constructions. Holliday junctions are accordingly parts of numerous such DNA structures. As confined Holliday junction edifices are too adaptable to even consider gathering into enormous arranged clusters, underlying themes with numerous Holliday junctions are utilized to make inflexible “tiles” that would then be able to collect into bigger “exhibits”